Enterprise value, or firm value, market value, market capitalization, and other methods may be used in different circumstances or compared to one another for contrast. For example, enterprise value would look at the market value of the company’s equity plus its debt, whereas book value per share only looks at the equity on the balance sheet. Conceptually, book value per share is similar to net worth, meaning it is assets minus debt, and may be looked at as though what would occur if operations were to cease. One must consider that the balance sheet may not reflect with certain accuracy, what would actually occur if a company did sell all of their assets.
- However, because assets would hypothetically sell at market value instead of historical asset values, this may not be an entirely accurate measurement.
- By repurchasing 1,000,000 common shares from the company’s shareholders, the BVPS increased from $3.00 to $4.50.
- By analyzing BVPS, investors can gain insights into a company’s financial health and intrinsic value, aiding in the assessment of whether a stock is over or undervalued.
- If the company’s BVPS increases, investors may consider the stock more valuable, and the stock’s price may increase.
Petition to ‘hold leader to account’
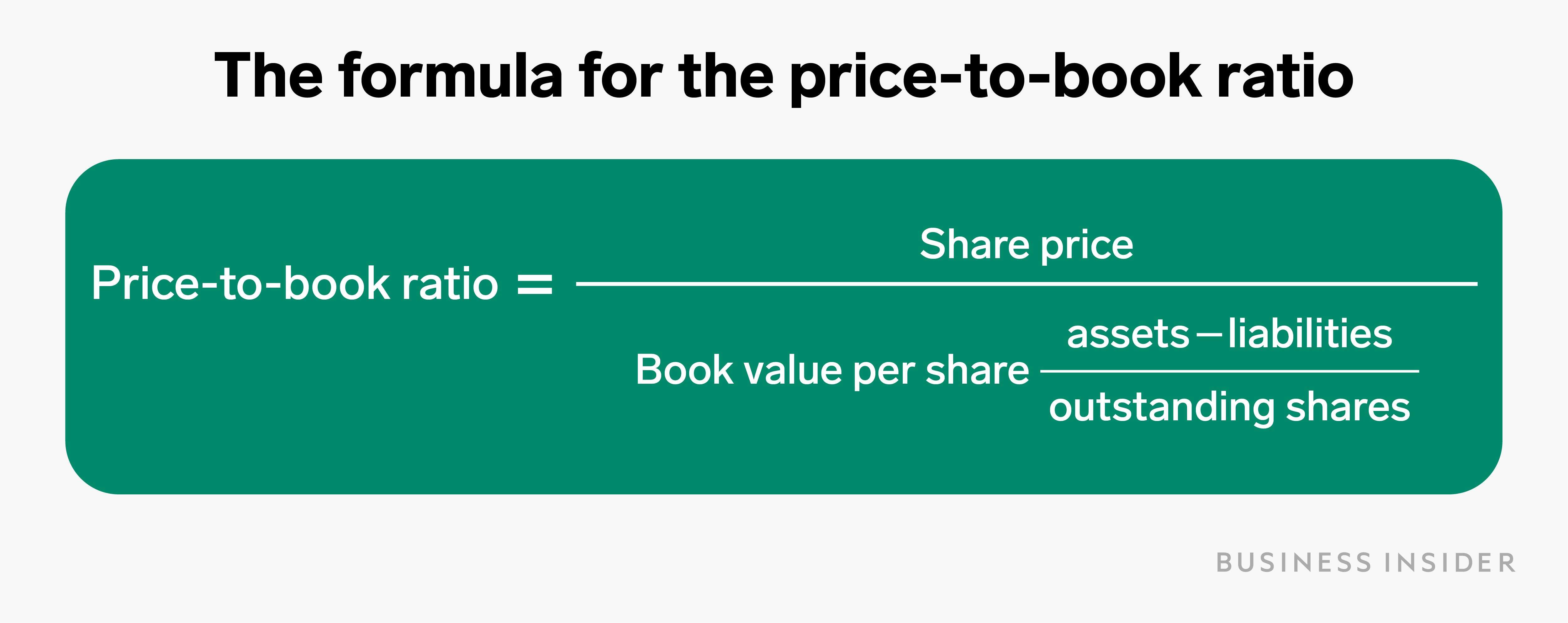
Critics of book value are quick to point out that finding genuine book value plays has become difficult in the heavily-analyzed U.S. stock market. Oddly enough, this has been a constant refrain heard since the 1950s, yet value investors continue to find book value plays. The answer could be that the market is unfairly battering the company, but it’s equally probable that the stated book value does not represent the real value of the assets.
Book Value Per Share Calculation Example (BVPS)
This is especially applicable when the analyst has low visibility of the company’s future earnings prospects. In other words, investors understand the company’s recent performance is underwhelming, but the potential for a long-term turnaround and the rock-bottom price can create a compelling margin of safety. The ratio may not serve as a valid valuation basis when comparing companies from different sectors and industries because companies in other industries may record their assets differently. If the market price for a share is higher than the BVPS, then the stock may be seen as overvalued.
How to Calculate BVPS?
While corporate debt holders and preferred shareholders are entitled to a fixed series of cash payments, the cash flow in excess of those amounts is essentially the property of the common shareholders. The value of a common stock, therefore, is related to the monetary value of the common shareholders’ residual claim on the corporation – the net asset value or common equity of the corporation. As a result, investors must first determine the market capitalisation of a company by multiplying the current market price of its stocks by the total number of outstanding shares.
Is a negative P/B ratio good?
The book value of a company is the difference between that company’s total assets and total liabilities, and not its share price in the market. The price-to-book ratio measures the market valuation of the company compared to its book value. A business is usually seen as beneficial for investment if its P/B ratio is 1 or less. To understand what is PB ratio in share market deeply, keep reading this detailed guide ahead.
For example, let’s say that ABC Corporation has total equity of $1,000,000 and 1,000,000 shares outstanding. This means that each share of stock would be worth $1 if the company got liquidated. If quality assets have been depreciated faster than the drop in their true market value, you’ve found a hidden value that may help hold up the stock price in the future. If assets are being depreciated slower than the drop in market value, then the book value will be above the true value, creating a value trap for investors who only glance at the P/B ratio.
Whereas some price models and fundamental analyses are complex, calculating book value per share is fairly straightforward. At its core, it’s subtracting a company’s preferred stock from shareholder equity and dividing that sum by the average amount of outstanding shares. Because book value per share only considers the book value, it fails to incorporate other intangible factors that may increase the market value of a company’s shares, even upon liquidation.
Investors can compare BVPS to a stock’s market price to get an idea of whether that stock is overvalued or undervalued. In the example from a moment ago, a how to accept payments online company has $1,000,000 in equity and 1,000,000 shares outstanding. Now, let’s say that the company invests in a new piece of equipment that costs $500,000.
Book Value per Share (BVPS) is the ratio of a company’s equity available to common shareholders to the number of outstanding company shares. This ratio calculates the minimum value of a company’s equity and determines a firm’s book value, or Net Asset Value (NAV), on a per-share basis. In other words, it defines the accounting value (i.e. book value) of a share of a company’s publicly-traded stock. Book Value Per Share (BVPS) is a crucial financial metric that indicates the per-share value of a company’s equity available to common shareholders.
A host of factors are at play at any point in time that can affect the P/B ratio of a particular company, sector, and even industry. Therefore, common and fundamental parameters must first be sorted out before using this ratio as a basis for investment decisions. However, investors should note that finding BVPS in isolation cannot produce promising analysis. It can be used in conjunction with other metrics like Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) and Price-to-earnings ratio (PE) to reach a somewhat concrete view of an organisation’s potential.